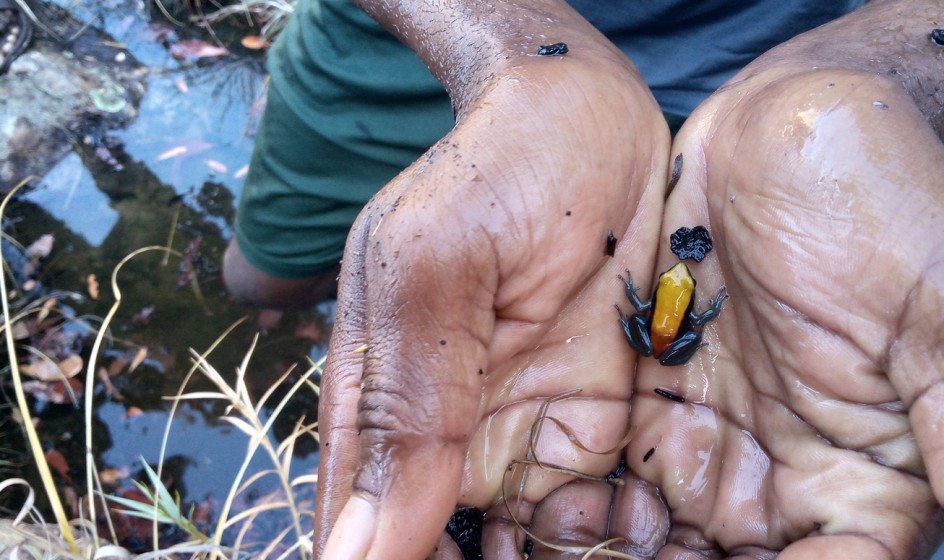


Blue-legged Mantella
Establishing a captive insurance population for the highly endangered yellow mantella in western Madagascar
The blue-legged mantella (Mantella expectata) is an Endangered species on the IUCN Red List and endemic to the National Park Isalo. Due to ongoing habitat loss the species is still in decline. In order to create an insurance population the project team of the University of Mahajanga plans to establish a captive breeding programme for the species.
In 2021, an amphibian captive breeding center has been opened in the western part of Madagascar thanks to a previous grant by Stiftung Artenschutz. The goal of this center is to contribute to the conservation of all endangered species in western Madagascar. Given the threats weighing on Mantella expectata, this will be second species managed in the centre after the green mantella (M. viridis), benefitting from the experience the centre has collected so far, amongst others by cooperation and exchange with national and international experts.
Before collecting the founder animals, biological, ecological and behavioral studies will be carried out in the wild to be able to replicate the conditions animals need to thrive. One of the crucial activities will be insect rearing for food provision, hence the project aims to build more capacity here.
The long-term goal of the project is to establish a sustainable breeding colony, alongside with conducting in situ habitat protection measures, so that reintroductions are possible in the future.
Species:
Blue-legged mantella (Mantella expectata)
Country:
Madagascar
Implementing Partner:
University of Mahajanga
Funding period:
Jan 2022 - Dec 2022
Project goals
- To understand the biology, ecology and behaviour of the species in the wild
- To establish an insurance population of Mantella expectata
Planned activities
- To survey and monitor the species in their natural habitat
- To characterize the species habitat, especially the reproduction sites (biotic and abiotic factors)
- To observe focal individuals to understand their behavior
- To prepare the necessary housing (including biosecurity and food supply) for the frogs in the breeding centre, according to the information collected in the wild